Data engineering 101: Understanding the Fundementals
In this article we will explore the different aspects of data engineering and what makes it crucial in today’s data-driven world and how it can benefit organizations of all sizes and industries.
So let’s get started!
Contents
- What is Data Democratization?
- What is Data Engineering?
- Role of Data Engineer
- Data Engineering vs Big Data Engineering
- Data Flow
- Recap
- Resources
What is Data Democratization?
Data democratization is the process of making data accessible to all members of an organization, regardless of their role or level of technical expertise. It enables organizations to make better and more informed decisions by providing access to data to a wide range of users. Data democratization also helps to promote data-driven culture within an organization, as it enables them to explore and leverage their data to create new products and services.
What is Data Engineering?
While data democratization is the foundation for organizations to become data-driven and make better decisions, data engineering plays a vital role in making it happen.
Data engineering is the process of acquiring, storing, and preparing raw data for analysis to extract valuable insights from their data and make informed business decisions.
Role of Data Engineer
A data engineer is responsible for the “plumbing” that helps derive value from data. The specific responsibilities of a data engineer may vary depending on the organization and industry, but generally include:
- Designing and building data pipelines
- Acquire data from various sources into the appropriate storage and processing systems
- Coordination of the many jobs through orchestration tools
- Data storage and management
- Work with different types of data storage systems
- Design and implement data models
- Data processing
- Work with different types of data processing methods such as batch processing and streaming processing
- Data governance
- Ensure data is accurate, reliable, and easily accessible to users
- Establish, implement, and maintain policies and procedures for data quality, compliance, and security
- Manage data infrastructure
- Collaboration and communication
- Work closely with data scientists, analysts, and other stakeholders to understand their data needs and develop solutions that meet their requirements
- Communicate with other teams such as DevOps, IT and security to ensure that the data infrastructure is aligned with the organization’s overall strategy
Data Engineering vs Big Data Engineering
According to a study by IDC, the global data sphere is projected to grow from 33 zettabytes (ZB) in 2018 to 175 ZB by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate of 23%. It’s also important to note that the vast majority of this data (about 90%) is unstructured data, such as social media posts, images, and videos. Another study by IBM estimates that 2.5 quintillion bytes of data are created every day, and this amount is increasing exponentially.
These statistics highlight the sheer volume of data that is being generated on a daily basis and the significant growth in the amount of data generated over time which leads us to the definition of Big Data.
Big data refers to extremely large and complex data sets that are difficult to process and analyze using traditional data processing and management techniques. These data sets are characterized by the “3Vs” - volume, velocity, and variety.
- Volume refers to the sheer amount of data that is generated and collected, this could be in terabytes, petabytes, or even exabytes.
- Velocity refers to the speed at which data is generated and collected. With the growing number of devices and sensors that are connected to the internet, data is being generated at an unprecedented rate.
- Variety refers to the different types of data that are generated and collected, such as structured data, unstructured data, and semi-structured data.
So is data engineering always “Big”?
Data engineering is the broader concept of designing, building, and maintaining systems and infrastructure to support data-driven applications and services, while big data engineering is a specific subfield that is focused on the management and analysis of extremely large and complex data sets that requires the use of advanced processing tools and analytics techniques.
Overall, data engineering is needed to democratize data inside an organization for informed business decisions, not just when we are dealing with big data.
After understanding the “What” and the “Why” behind data engineering, it is now time to delve into the “How” of data engineering.
Data Flow
The data flow outlines the different stages involved in making data easily accessible in a reliable and accurate way for analysis and decision making.
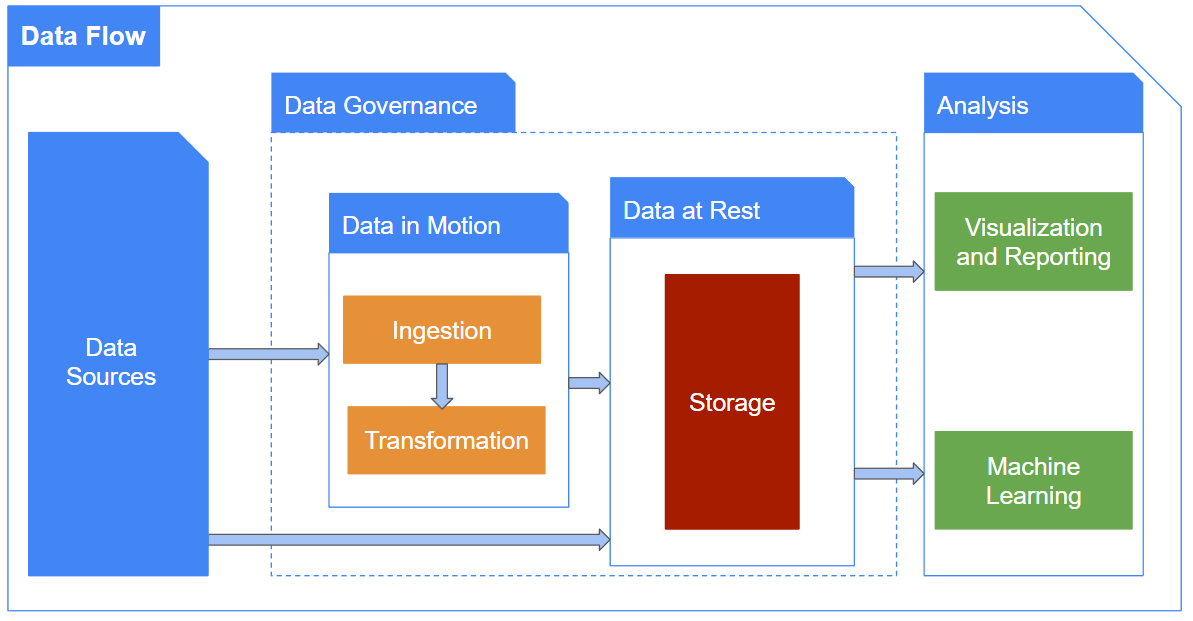
The general steps include:
- Data Sources
- Data sources are an important and challenging step due to the wide range of potential integration points.
- Depending on the organization’s needs, some common data sources include:
- Relational and non relational databases
- Flat files: Data stored in CSV, Excel, or other flat file formats
- Streaming data: Data generated in real-time, such as data from social media feeds or IoT devices
- External data: Data from third-party sources, such as government data or data from other companies
- Legacy systems: Data stored in older systems that need to be migrated to the new data infrastructure
-
Data Governance
Data governance is the systematic management of the availability, usability, integrity and security of the data used in an organization. It is not particularly a separate step in the data flow, but rather a broad concept that involves processes, people and technology that support these processes in order to maintain high quality data and make better data driven decisions. - Data in Motion
- Ingestion
Ingestion is the process of acquiring and importing data from various sources into the organization’s data infrastructure. - Transformation
This is the process of cleaning, normalizing, and transforming the data acquired during the ingestion step so that it is in a format that can be used for analysis and reporting.
- Ingestion
-
Data at Rest: Storage
This is the process of storing and managing the data in a way that it can be accessed, queried, and updated easily. Therefore, choosing the right type of storage and technology is a key element not only to the following steps, but also to previous ones due to the fact that we might require multiple storages in different steps. - Analysis
This is the step where we extract insights and knowledge from the processed data. This involves:- Visualization and Reporting
Creating visual representations of the data to help communicate insights and make it easy to understand - Machine learning
Using algorithms to learn from the data
- Visualization and Reporting
Recap
In this article we have seen how valuable it is to democratize data inside an organization to make the shift towards data-driven decision making and the main role played by data engineers in the different steps of the raw data goes through to reach this goal. In the following blog post we will dive deeper into each step to uncover best practices, tools and paradigms used and how they have evolved in an ever changing field. Stay tuned!
Happy learning!
Resources
https://medium.com/free-code-camp/the-rise-of-the-data-engineer-91be18f1e603
https://maximebeauchemin.medium.com/the-downfall-of-the-data-engineer-5bfb701e5d6b