Data engineering 201: In-depth Guide - Part 1
In this two parts article we will deep dive into each of the general steps of the data flow.
In a previous blog post, we saw the importance of data engineering in democratizing data inside an organization and enabling data driven decision making. In addition, we outlined the different stages data goes through in order to be able to extract insights out of it.
Here is a reminder of our data flow blueprint:
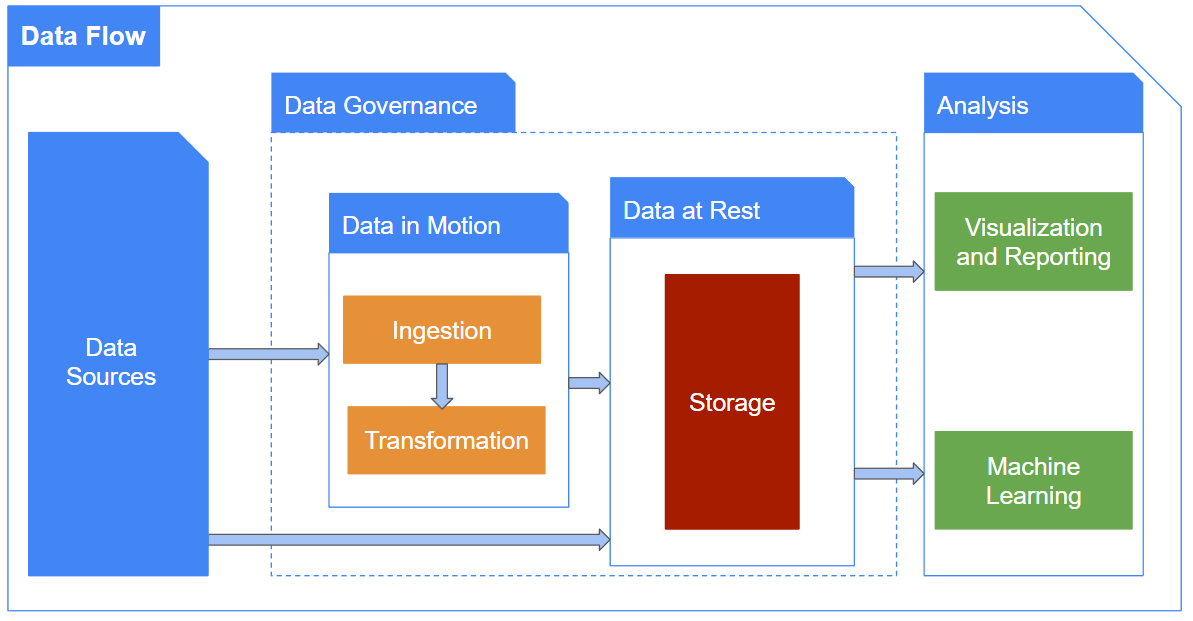
We will start by taking a bird’s eye view, focusing on data sources, data governance and analysis before zooming in on the other stages of the data flow in part 2.
So let’s get started!
Contents
Data Sources
Data sources refer to the various systems and platforms that generate data and constitute the origin of all data in an organization and play a crucial role in the data engineering and big data landscape. These sources can be internal systems such as transactional databases, or external sources such as social media platforms, sensors, or log files.
The variety and volume of data sources have dramatically increased with the growth of big data, making it important for organizations to have a comprehensive strategy for managing, processing, and analyzing data from multiple sources.
For instance, data must be transformed and stored in a format that enables efficient processing and analysis. There are a variety of file formats, such as Parquet and Avro, that are common to big data use cases and which provide a means of storing and exchanging large volumes of structured and semi-structured data in a standardized way, making it easier for organizations to work with data from multiple sources.
Following is a table summarizing some properties and how do they compare between some big data file formats:
| Properties | CSV | JSON | Parquet | Avro |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human readability | Yes | Yes | No | NO |
| Format | Row-based | Key-Value | Columunar | Row-based |
| Compressible | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Splittable | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Complex data structure | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Schema evolution | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Read performance | Slow | Slow | Fast | Average |
| Write performance | Fast | Fast | Slow | Average |
Table 1: Big Data File Formats Properties Comparison
CSV should typically be the fastest to write, JSON the easiest to understand for humans, and Parquet the fastest to read a subset of columns, while Avro is the fastest to read all columns at once.
Data Governance
Data governance is the systematic management of the availability, usability, integrity and security of the data used in an organization. It includes the actions people must take, the processes they must follow, and the technology that supports them throughout the data lifecycle to ensure data is secure, private, accurate, available, and usable.
Some of the key components of the data governance include:
- Data compliance: Establishing clear policies, procedures, and standards to govern data collection, storage, and usage. In addition, regularly monitoring and auditing data to ensure compliance with relevant regulations and laws
- Data security: Implementing security measures to protect data from unauthorized access and breaches.
- Data privacy: Ensuring that personal and confidential data is managed in accordance with relevant regulations and laws.
- Data Quality: Refers to the development and implementation of activities that apply quality management techniques to data to make sure it is suitable to be used in a specific context, thus considered to be high quality data. Data quality is generally judged on six dimensions: accuracy, completeness, consistency, timeliness, validity, and uniqueness.
- Data cataloging: Maintaining a comprehensive and up-to-date inventory of data assets, including metadata, definitions, and relationships.
- Data lineage: Tracing the origin and evolution of data to understand its history and potential impact on decision-making.
Data Governance vs Data Management
The scope of Data management is broader than data governance. Data management includes all aspects of the full data lifecycle from collection and storage to usage and oversight. This is inclusive of data governance, which can be considered as a core component of it, but it also includes other areas such as data architecture and data modeling.
Benefits of Data Governance
Implementing a data governance framework can increase the value of data within your organization and therefore make better and more timely decisions. In fact, effective data governance aims to maintain high quality data that’s both secure and compliant and easily accessible for deeper business insights.
Analysis
Visualization and reporting play a critical role in helping organizations to make informed decisions. By presenting data in an easily understandable format, stakeholders can gain insights into trends, patterns, and relationships that would not be evident from raw data alone. Effective visualization and reporting also make it easier for organizations to communicate the results of data analysis to others, including stakeholders, partners, and customers.
Visualization is the process of creating visual representations of data and information, such as charts, graphs, and maps. Data visualization can be done using a wide range of tools including plotting libraries such as matplotlib or seaborn which are used especially by data scientists to more powerful analytics dashboards such as Tableau and Microsoft Power BI.
Reporting, on the other hand, is the presentation of data and information in a structured format that is designed to be easily consumable by stakeholders. Reports are often used to provide an overview of key metrics, trends, and insights, and can be used to support decision making and strategic planning.
Another aspect of the data analysis we mentioned in this article is the use of machine learning algorithms. However, it is not feasible to fully cover the topic of machine learning within the scope of this article. Though a good starting point for anyone new to this field is the machine learning specialization course from Andrew Ng.
With this we have reached the end of this post, I hope you enjoyed it!
Recap
In this article we saw the different types of big data file formats and how they compare to each other which can help shape our choice to achieve more efficient data processing. In addition, we discussed some of the key components of data governance and its benefit to achieve better data quality and therefore better data analysis through the usage of visualization and reporting.
Happy learning!
Resources
https://devopedia.org/data-serialization
https://cloud.google.com/learn/what-is-data-governance
https://www.ibm.com/topics/data-governance
https://www.heavy.ai/technical-glossary/data-quality
https://www.tableau.com/learn/articles/data-management-vs-data-governance